[Very Important LLM System Design #14] MCP : How Model Context Protocol Actually Works- Part 14
All the technical details you need to know...
What Happens When Your LLM Needs to Access External Data?
When you ask an LLM to “check my calendar and suggest meeting times,” a complex integration challenge unfolds. Your AI assistant needs to securely connect to your calendar service, understand its data format, authenticate properly, and retrieve information in real-time. Traditionally, each integration required custom code, specific API implementations, and ongoing maintenance.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) changes everything by providing a universal standard for LLM-external system communication.
The Complete MCP Architecture Overview
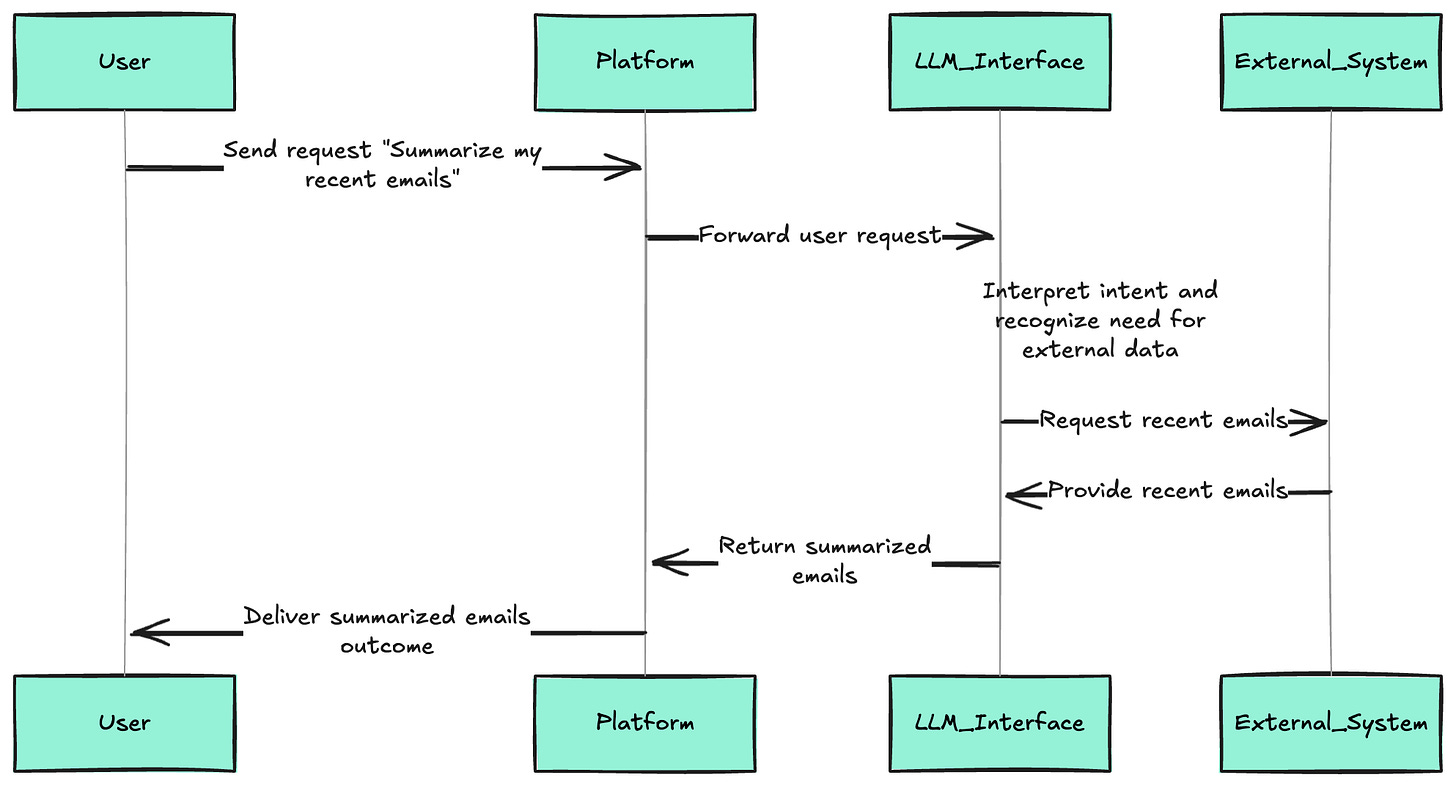
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ MCP ARCHITECTURE FLOW │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 1. USER INTERACTION │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ User: “Summarize my recent emails”│ │
│ │ Context: Needs external data │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ↓ │
│ │
│ 2. LLM PROCESSING (< 50ms) │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Intent Recognition: │ │
│ │ • Identifies need for email data │ │
│ │ • Determines MCP resource required│ │
│ │ • Prepares context request │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ↓ │
│ │
│ 3. MCP CLIENT REQUEST (< 10ms) │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Protocol: JSON-RPC 2.0 │ │
│ │ Method: “resources/read” │ │
│ │ Params: { │ │
│ │ “uri”: “email://inbox/recent”, │ │
│ │ “filter”: “last_7_days” │ │
│ │ } │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ↓ │
│ │
│ 4. MCP SERVER PROCESSING (< 100ms) │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ • Validates authentication │ │
│ │ • Connects to email service │ │
│ │ • Retrieves and formats data │ │
│ │ • Returns structured response │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ↓ │
│ │
│ 5. CONTEXT INJECTION (< 20ms) │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Email data injected into LLM │ │
│ │ context window: │ │
│ │ • Subject lines │ │
│ │ • Sender information │ │
│ │ • Brief content summaries │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ↓ │
│ │
│ 6. LLM GENERATION (< 200ms) │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ “You have 23 emails this week. │ │
│ │ Key highlights: │ │
│ │ • Project deadline reminder │ │
│ │ • Client meeting request │ │
│ │ • Team update from Sarah...” │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
│ Total Latency: 380ms for complete flow ⚡ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Understanding MCP: What Is It?
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open protocol that standardizes how AI applications provide context to Large Language Models. Developed by Anthropic and released as an open standard, MCP solves the fundamental challenge of connecting LLMs to external data sources, tools, and services in a secure, scalable, and maintainable way.
Read previous parts -
Understanding Transformers & Large Language Models: How They Actually Work - Part 1
Understanding Transformers & Large Language Models: How They Actually Work - Part 2
[LLM System Design #3] Large Language Models: Pre-Training LLMs: How They Actually Work - Part 3
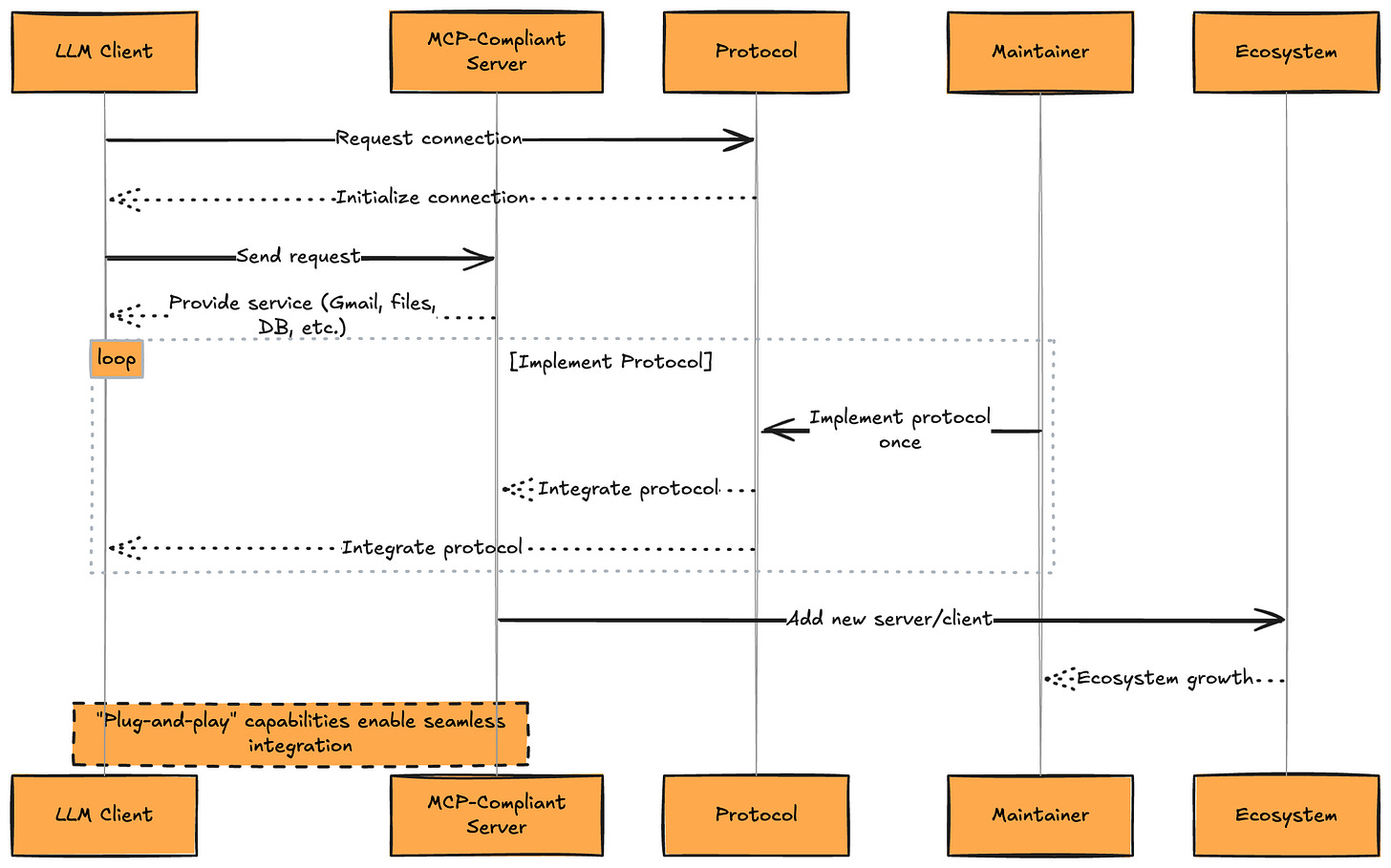
The Core Challenge: Integration Complexity
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ THE PRE-MCP INTEGRATION PROBLEM │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ Traditional Approach (The Old Way): │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ LLM Application │ │
│ │ ↓ ↓ ↓ │ │
│ │ Custom Custom Custom │ │
│ │ Code #1 Code #2 Code #3 │ │
│ │ ↓ ↓ ↓ │ │
│ │ Gmail API Slack API DB API │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ Problems: │ │
│ │ • Each integration needs custom code│ │
│ │ • No standardization │ │
│ │ • Difficult to maintain │ │
│ │ • Security concerns │ │
│ │ • Doesn’t scale │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
│ MCP Approach (The New Way): │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ LLM Application │ │
│ │ ↓ │ │
│ │ MCP CLIENT │ │
│ │ ↓ │ │
│ │ Standard Protocol │ │
│ │ ↓ ↓ ↓ │ │
│ │ MCP MCP MCP │ │
│ │ Server Server Server │ │
│ │ ↓ ↓ ↓ │ │
│ │ Gmail Slack DB │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ Benefits: │ │
│ │ • Universal standard protocol │ │
│ │ • Plug-and-play integrations │ │
│ │ • Easy maintenance │ │
│ │ • Built-in security │ │
│ │ • Highly scalable │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Core MCP Concepts
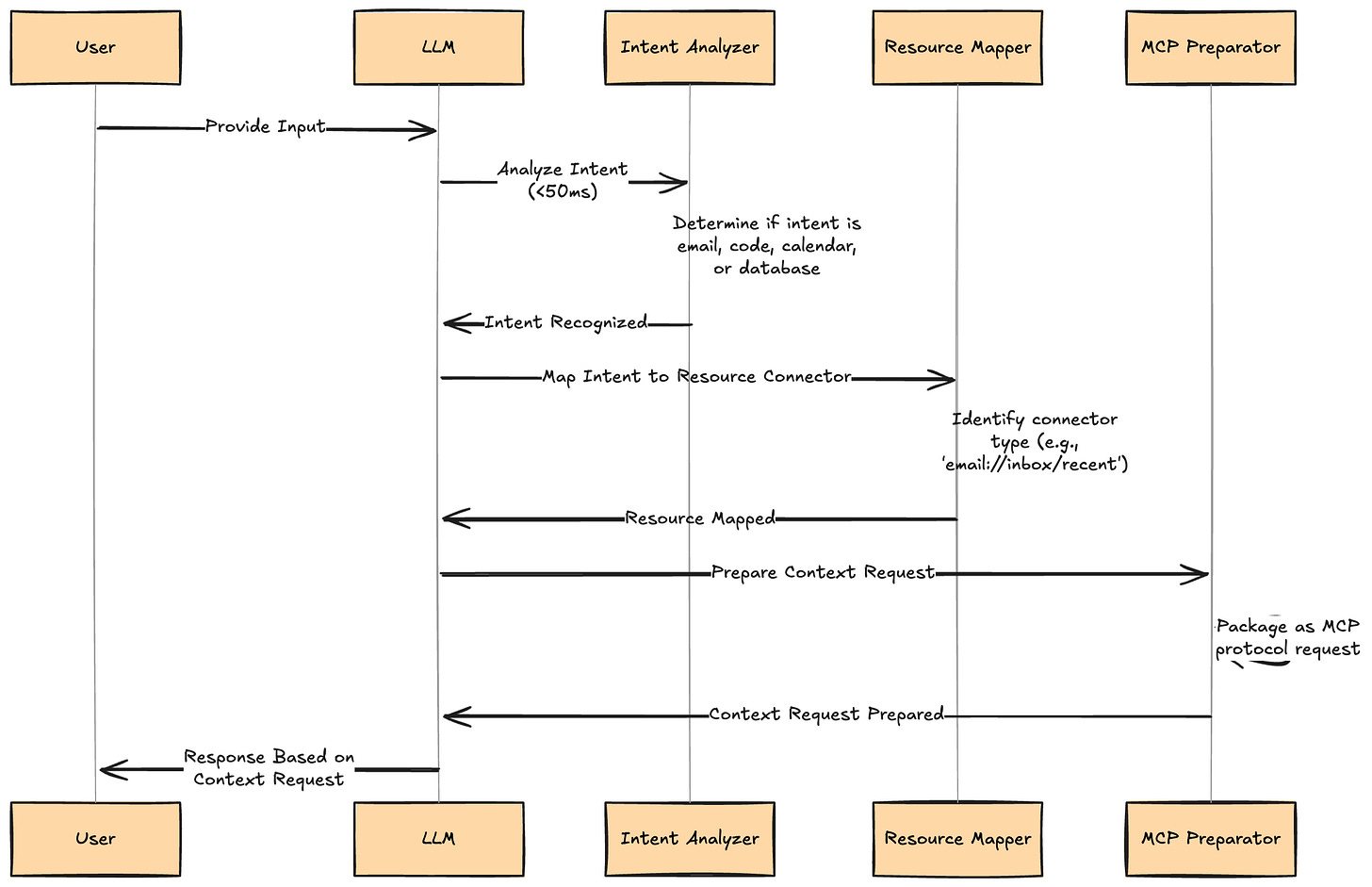
1. User Interaction
How it works:
Everything starts with a user’s request, such as “Summarize my recent emails.” The LLM interface receives this, usually via a chat or voice platform, where the intent and the need for external data are implicit. The user isn’t required to know the technicalities—just what outcome is desired.
Below are the top 10 System Design Case studies for this week
Billions of Queries Daily : How Google Search Actually Works
100+ Million Requests per Second : How Amazon Shopping Cart Actually Works
Serving 132+ Million Users : Scaling for Global Transit Real Time Ride Sharing Market at Uber
3 Billion Daily Users : How Youtube Actually Scales
$100000 per BTC : How Bitcoin Actually Works
$320 Billion Crypto Transactions Volume: How Coinbase Actually Works
100K Events per Second : How Uber Real-Time Surge Pricing Actually Works
Processing 2 Billion Daily Queries : How Facebook Graph Search Actually Works
7 Trillion Messages Daily : Magic Behind LinkedIn Architecture and How It Actually Works
1 Billion Tweets Daily : Magic Behind Twitter Scaling and How It Actually Works
12 Million Daily Users: Inside Slack’s Real-Time Messaging Magic and How it Actually Works
3 Billion Daily Users : How Youtube Actually Scales
1.5 Billion Swipes per Day : How Tinder Matching Actually Works
500+ Million Users Daily : How Instagram Stories Actually Work
2.9 Billion Daily Active Users : How Facebook News Feed Algorithm Actually Works
20 Billion Messages Daily: How Facebook Messenger Actually Works
8+ Billion Daily Views: How Facebook’s Live Video Ranking Algorithm Works
How Discord’s Real-Time Chat Scales to 200+ Million Users
80 Million Photos Daily : How Instagram Achieves Real Time Photo Sharing
Serving 1 Trillion Edges in Social Graph with 1ms Read Times : How Facebook TAO works
How Lyft Handles 2x Traffic Spikes during Peak Hours with Auto scaling Infrastructure..
Why it matters:
Users expect an assistant to fetch their information and reason about it naturally, but behind the scenes, this requires complex integrations and secure access to external data. This stage is about seamless natural language input leading to advanced technical orchestration.
2. LLM Processing
How it works:
As soon as the LLM receives the user input, it runs a fast (sub-50ms) analysis to determine intent: