[System Design Tech Case Study Pulse #49] 100+ Million Requests per Second : How Amazon Shopping Cart Actually Works
With detailed explanation and flow chart....
Hi All,
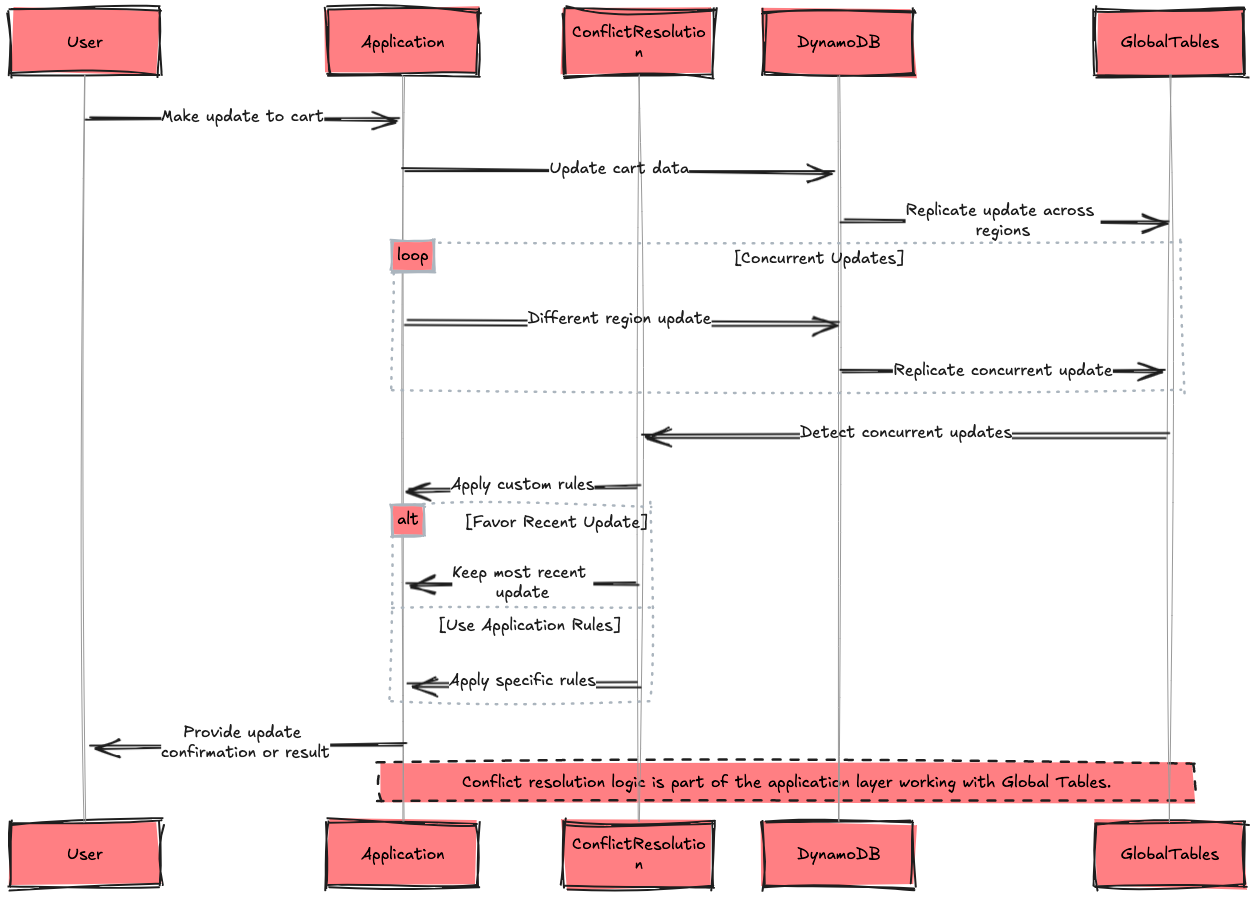
Amazon's implementation of DynamoDB plays a crucial role in managing their shopping cart system, handling an astounding 100 million+ requests per second during peak times. This feat enables Amazon to provide a seamless, low-latency shopping experience for millions of customers worldwide, even during high-traffic events like Prime Day.
Learn how to System design —Design Lyft
Let me dive deep into how Amazon engineered this system, exploring the key architectural decisions, scaling strategies, and optimizations that enable DynamoDB to manage this enormous volume of shopping cart data and requests.
System Overview
Before we delve into Amazon's DynamoDB architecture for the shopping cart system, let's look at some key metrics that highlight the scale of its operations:
- Requests per second: 100 million+
- Active users: Hundreds of millions
- Items in catalog: 350 million+
- Peak operations: Black Friday, Prime Day
- Data centers: Multiple, globally distributed
- Latency target: < 10 milliseconds
- Availability: 99.999%+
- Supported devices: Web, mobile, smart devices
- DynamoDB tables: Hundreds, purpose-specific
- Total data managed: Petabytes
Learn system design pulses -
[System Design Pulse #3] THE theorem of System Design and why you MUST know it - Brewer theorem
[System Design Pulse #4] How Distributed Message Queues Work?
[System Design Pulse #5] Breaking It Down: The Magic Behind Microservices Architecture
[System Design Pulse #6] Why Availability Patterns Are So Crucial in System Design?
[System Design Pulse #7] How Consistency Patterns helps Design Robust and Efficient Systems?
[System Design Pulse #9] Why these Key Components are Crucial for System Design.