[System Design Pulse #21] Caching is Crucial : How Caching Slashes Latency and Supercharges Performance
And why Caching is so crucial...
Hi all,
In this post I’m going to cover the silent hero of modern computing: caching. It's the secret sauce that keeps your favorite apps snappy, your websites loading in the blink of an eye, and your databases humming along without breaking a sweat.
Imagine if every time you wanted a snack, you had to drive to the grocery store. That's what computing would be like without caching! Instead, caching is like having a well-stocked pantry right in your kitchen. It's all about keeping frequently accessed data close at hand, ready to serve up at a moment's notice.
Today we will cover -
1. Introduction to Caching
2. Types of Caching
2.1 Client Caching
2.2 CDN Caching
2.3 Web Server Caching
2.4 Database Caching
2.5 Application Caching
3. Cache Invalidation Strategies
3.1 Cache Aside
3.2 Write Through
3.3 Write Behind (Write Back)
3.4 Refresh Ahead
4. Flowcharts for Caching
5. Real World Application Example: E commerce Website
5.1 Client Caching in E commerce
5.2 CDN Caching in E commerce
5.3 Web Server Caching in E commerce
5.4 Database Caching in E commerce
5.5 Application Caching in E commerce
6. Cache Strategies in E commerce
7. Story Analogy ( with real world)
System Design Github - Link
Learn system design pulses -
[System Design Pulse #3] THE theorem of System Design and why you MUST know it - Brewer theorem
[System Design Pulse #4] How Distributed Message Queues Work?
[System Design Pulse #5] Breaking It Down: The Magic Behind Microservices Architecture
[System Design Pulse #6] Why Availability Patterns Are So Crucial in System Design?
[System Design Pulse #7] How Consistency Patterns helps Design Robust and Efficient Systems?
Lets get started —
Caching is used to improve the performance of systems by storing frequently accessed data in a temporary storage area, called a cache. This reduces the time and resources required to fetch data from the original source, leading to faster responses and reduced load on servers and databases.
Caching is a technique used to speed up data retrieval and reduce the load on servers by storing copies of frequently accessed data. Here’s a detailed look at various types of caching and how they work across different platforms.
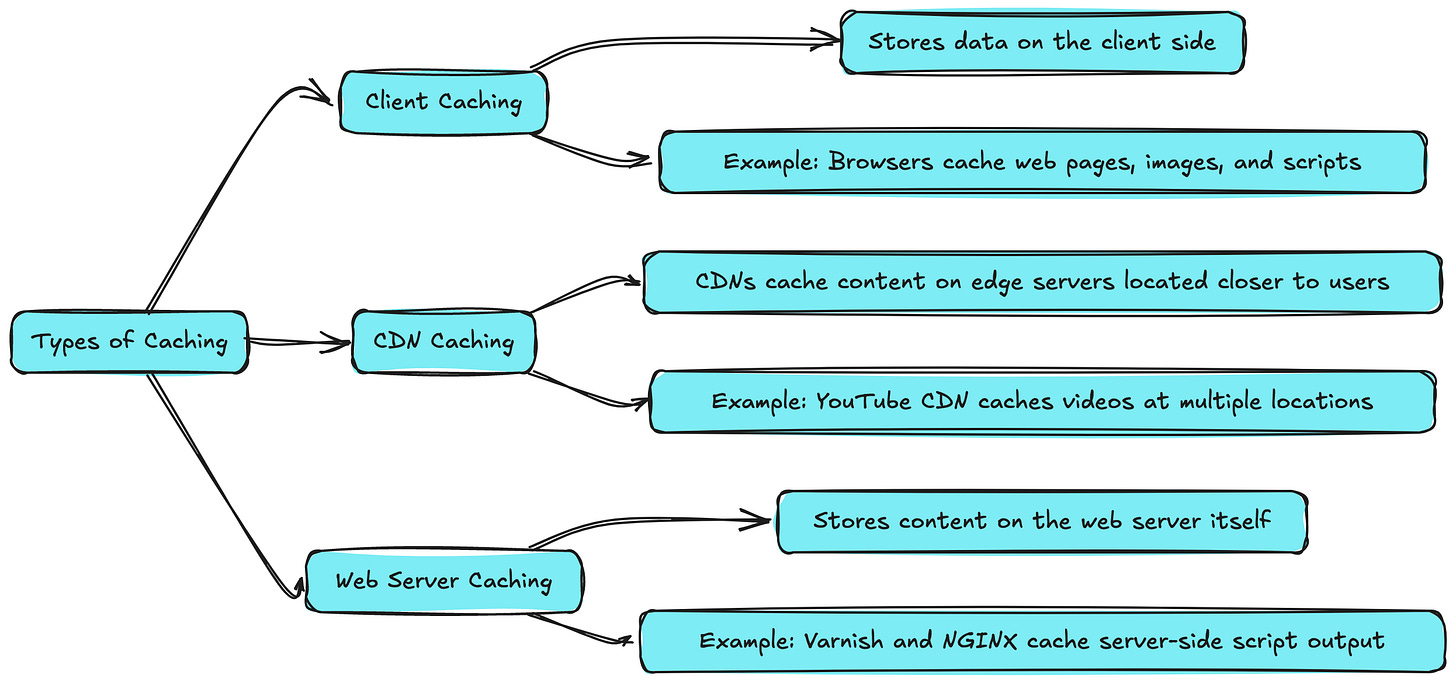
Types of Caching
1. Client Caching:
Stores data on the client side (e.g., in a web browser) to minimize the number of requests sent to the server.
Example : Browsers cache web pages, images, and scripts so that when you revisit a page, it loads faster.
2. CDN Caching:
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) cache content on edge servers located closer to users to reduce latency and improve load times.
Example : When you access a video on YouTube, the CDN caches it at multiple locations worldwide to deliver it quickly.