[Very Important Coding Interviews Series: Linked List #10] How To Solve ANY Linked List Programming Question ( Pattern Approach with Shortcuts): How it Works ( Implementation Code)
Everything you MUST know to solve any Linked List question...
This is the best hands-on guide you will ever find on Linked List and Advanced Linked List which follows Pattern based Approach to Solve any Linked List and Advanced Linked List Technique questions and Shortcuts You MUST READ and Implement.
Objective : Master all Linked List and Advanced Linked List patterns that appear in 100% of coding interview problems.
Table of Contents
Introduction
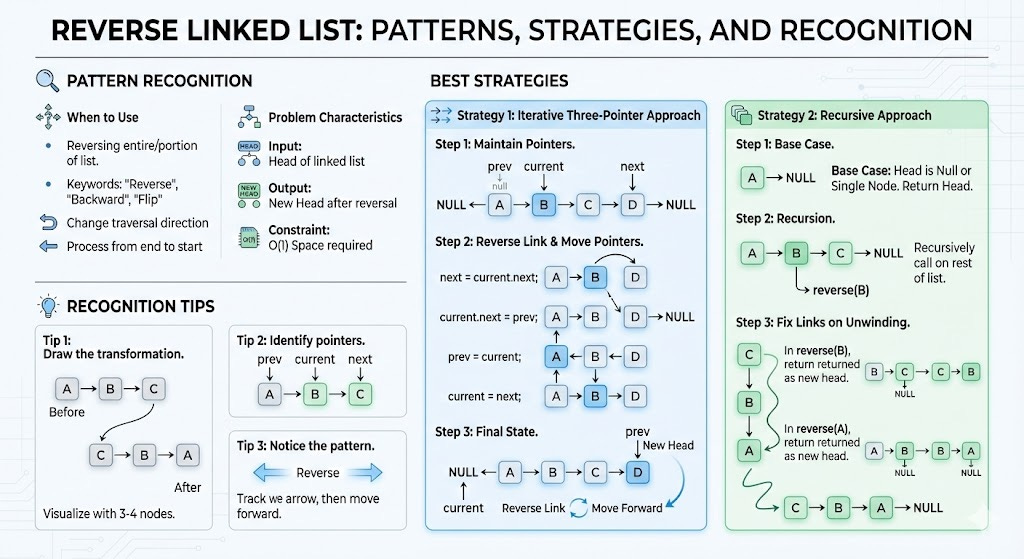
Pattern 1: Reverse Linked List (Iterative & Recursive)
Pattern 2: Fast & Slow Pointers (Floyd’s Cycle Detection)
Pattern 3: Merge Two or More Lists
Pattern 4: Two Pointers for Linked Lists
Pattern 5: In-Place Reversal of Sub-list
Pattern 6: Dummy Node Technique
Pattern 7: Reorder/Rearrange Lists
Pattern 8: Deep Copy with Random Pointers
Pattern 9: LRU Cache Design
Pattern 10: Remove Nodes
Shortcuts
Note : Each pattern comes with its Python Implementation ( can be found as you scroll) and at the end of thus post along with Linked List and Advanced Linked List Shortcuts and problem examples.
Practice your Interview with God Level Feedback Quantum —
On Quantum you can Practice FAANG-level questions with complete system design breakdowns, full architectures, trade-offs, and key concepts with God level feedback.
Also on live on product hunt - Quantum
Learn more patterns and shortcuts for each coding problem type —
Read ( major compilations of LLM System Design, ML System Design and 300+ Implemented Projects) —
[Important Bookmark] Compilation of All Implemented Projects ( with Code Implementation Files)
Introduction
Linked Lists are a fundamental data structure frequently tested in technical interviews at FAANG and other top tech companies. Unlike arrays, linked lists provide dynamic memory allocation and efficient insertion/deletion at any position. However, they lack random access and require pointer manipulation skills.
Key Characteristics:
Time Complexity: O(1) insertion/deletion (with pointer), O(n) search
Space Complexity: O(n) for n nodes
Common Pitfalls: Null pointer errors, losing references, memory leaks
Interview Success Strategy:
Always draw the list structure
Track multiple pointers carefully
Consider edge cases (empty, single node, two nodes)
Practice in-place operations to minimize space complexity