[Very Important Coding Interviews: Trees and Advanced Trees#08] How To Solve ANY Trees and Advanced Trees Programming Question ( Pattern Approach with Shortcuts) : How it Works ( Implementation Code)
Everything you MUST know to solve any Trees and Advanced Trees question...
This is the best hands-on guide you will ever find on Trees and Advanced Trees which follows Pattern based Approach to Solve any Trees and Advanced Trees questions and Shortcuts You MUST READ and Implement.
Objective : Master all Trees and Advanced Trees patterns that appear in 100% of coding interview problems.
Table of Contents
Tree Traversal Patterns
Level Order Traversal (BFS)
Tree Height and Depth
Tree Diameter
Balanced Tree Validation
Same Tree and Subtree
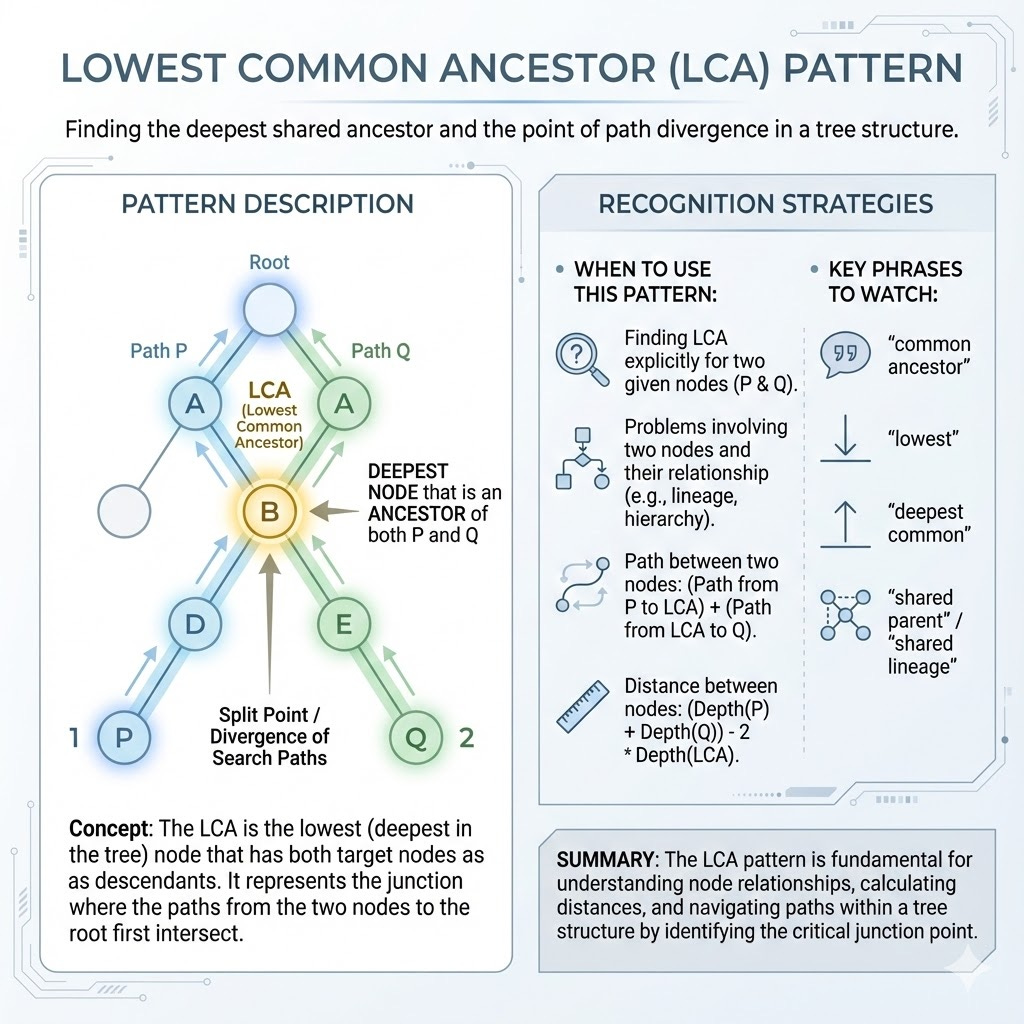
Lowest Common Ancestor (LCA)
Path Sum Patterns
Tree Construction
Serialize and Deserialize
Binary Search Tree (BST) Patterns
Trie (Prefix Tree)
Segment Tree
Binary Indexed Tree (Fenwick Tree)
Advanced Tree DP
Note : Each pattern comes with its Python Implementation ( can be found as you scroll) and at the end of thus post along with Trees and Advanced Trees Shortcuts and problem examples.
Practice your Interview with God Level Feedback Quantum —
On Quantum you can Practice FAANG-level questions with complete system design breakdowns, full architectures, trade-offs, and key concepts with God level feedback.
Also on live on product hunt - Quantum
Learn more patterns and shortcuts for each coding problem type —
Read ( major compilations of LLM System Design, ML System Design and 300+ Implemented Projects) —
[Important Bookmark] Compilation of All Implemented Projects ( with Code Implementation Files)
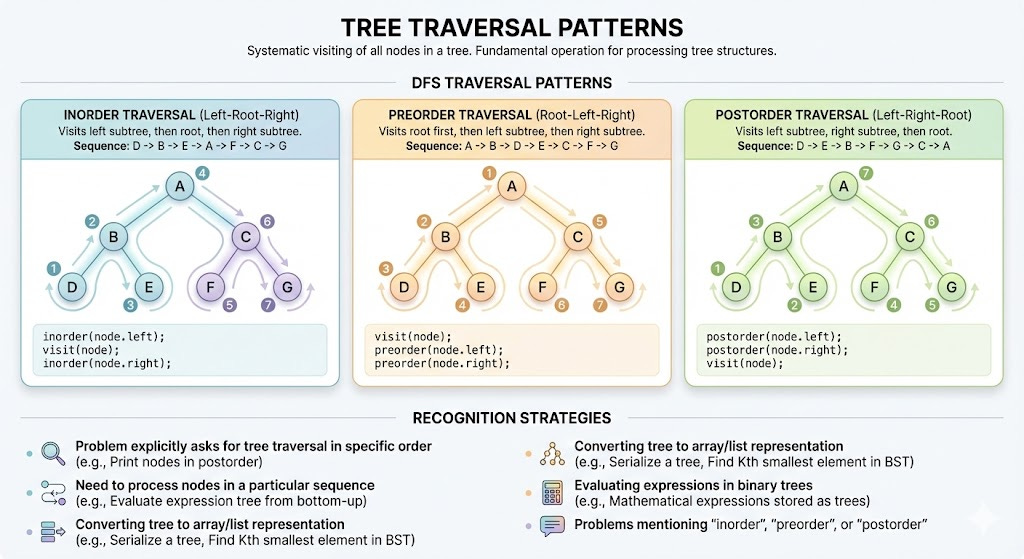
Tree Traversal Patterns
Pattern Description
Tree traversal is the fundamental operation of visiting all nodes in a tree systematically. The three main DFS traversal patterns are:
Inorder (Left-Root-Right): Visits left subtree, then root, then right subtree
Preorder (Root-Left-Right): Visits root first, then left subtree, then right subtree
Postorder (Left-Right-Root): Visits left subtree, right subtree, then root